Tape Cartridge Requirements
Tape Cartridge Requirements
Below figure 25 shows the types of tape cartridges that the tape library
supports, along with their densities and capacities. When loaded, the cartridges
automatically default to their highest supported density.
IBM recommends that you use DLTtape III XT and DLTtape IV tape cartridges.
Use of other tapes is not guaranteed. For information about ordering tape
cartridges, see 'Ordering Tape Cartridges'
 -Attention- If a prerecorded tape is reused and the Write From Beginning of Tape
(BOT) command is executed, all prerecorded data is lost (including the density setting).
-Attention- If a prerecorded tape is reused and the Write From Beginning of Tape
(BOT) command is executed, all prerecorded data is lost (including the density setting).
For read operation of prerecorded tape media, the recorded density will be read back.
For write operation, the tape media can be recorded using any of the supported densities of the loaded tape type from BOT, or using the default density
of the loaded tape type.
For write append operation, the prerecorded data density will be used.
Figure 25. Tape Cartridge Capacity and Density
Type of
Cartridge
Supported |
Density |
Compressed Data Capacity * |
| DLTtape IV |
20.0 GB
35.0 GB |
40.0 GB
70.0 GB (default for drive) |
| DLTtape III XT |
15.0 GB |
30.0 GB (default for drive) |
| DLTtape III |
2.6 GB
6.0 GB
10.0 GB |
2.6 GB (no compression)
6.0 GB (no compression)
20.0 GB (default for drive) |
Notes:
- The DLT7000 drive is sensitive to block size.
For example, using a block size of 1024 and backing up 32 GB of data takes approximately
22 hours; using a block size of 30,000 for the same amount of data takes approximately 2 hours.
Small block sizes have a significant impact on performance, but only a minimal impact on capacity.
However, 2.6 format (density) and 6 format (density) are significantly impacted in capacity
by using small block sizes because they do not pack the data in the internal block.
- Users should ensure the block size they select is supported by their application.
- * The amount of compression depends upon the type of data being compressed. A
compression ratio of 2:1 is assumed for this compressed capacity.
The cartridges can be labeled or unlabeled.
When the cartridges do not have a label, the host computer will identify the tape cartridge
by the information at the beginning of the tape.
Labels can be applied to the edge of a tape cartridge and used by the bar code reader to
identify the contents of the tape cartridge.
(For more information, see 'Tape Cartridge Labels'.)
Figure 26 shows a typical tape cartridge.
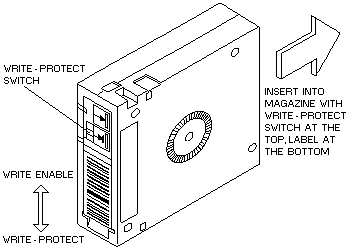
Figure 26. Tape Cartridge with Label
When preparing tapes for use in the tape library keep the following in mind:
- The write-protect switch must be set to the correct position for the intended purpose
of the tape cartridge, (see 'Write-Protect Switch').
- The tape leader block must be in the correct position before inserting the
cartridge into the tape library (see 'Tape Leader Check').
- The tape cartridge must be inserted vertically into the magazine, with the
write-protect switch at the top and the label at the bottom.
IBM recommends that data cartridges be retired after 10,000 loads to avoid
possible data reliability problems and load/unload problems.
Back to 
Please see the LEGAL - Trademark notice.
Feel free - send a  for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.
for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.
 -Attention- If a prerecorded tape is reused and the Write From Beginning of Tape
(BOT) command is executed, all prerecorded data is lost (including the density setting).
-Attention- If a prerecorded tape is reused and the Write From Beginning of Tape
(BOT) command is executed, all prerecorded data is lost (including the density setting).